🔢 Numerical Features
Transform your continuous data like age, income, or prices into powerful feature representations
📋 Quick Overview
Numerical features are the backbone of most machine learning models. KDP provides multiple ways to handle them, from simple normalization to advanced neural embeddings.
🎯 Types and Use Cases
| Feature Type | Best For | Example Values | When to Use |
|---|---|---|---|
FLOAT_NORMALIZED |
Data with clear bounds | 🧓 Age: 18-65, ⭐ Score: 0-100 | When you know your data falls in a specific range |
FLOAT_RESCALED |
Unbounded, varied data | 💰 Income: $0-$1M+, 📊 Revenue | When data has outliers or unknown bounds |
FLOAT_DISCRETIZED |
Values that form groups | 📅 Years: 1-50, ⭐ Ratings: 1-5 | When groups of values have special meaning |
FLOAT |
Default normalization | 🔢 General numeric values | When you want standard normalization (identical to FLOAT_NORMALIZED) |
🚀 Basic Usage
The simplest way to define numerical features is with the FeatureType enum:
from kdp import PreprocessingModel, FeatureType
# ✨ Quick numerical feature definition
features = {
"age": FeatureType.FLOAT_NORMALIZED, # 🧓 Age gets 0-1 normalization
"income": FeatureType.FLOAT_RESCALED, # 💰 Income gets robust scaling
"transaction_count": FeatureType.FLOAT, # 🔢 Default normalization
"rating": FeatureType.FLOAT_DISCRETIZED # ⭐ Discretized into bins
}
# 🏗️ Create your preprocessor
preprocessor = PreprocessingModel(
path_data="customer_data.csv",
features_specs=features
)
🧠 Advanced Configuration
For more control, use the NumericalFeature class:
from kdp.features import NumericalFeature
features = {
# 🧓 Simple example with enhanced configuration
"age": NumericalFeature(
name="age",
feature_type=FeatureType.FLOAT_NORMALIZED,
use_embedding=True, # 🔄 Create neural embeddings
embedding_dim=16, # 📏 Size of embedding
preferred_distribution="normal" # 📊 Hint about distribution
),
# 💰 Financial data example
"transaction_amount": NumericalFeature(
name="transaction_amount",
feature_type=FeatureType.FLOAT_RESCALED,
use_embedding=True,
embedding_dim=32,
preferred_distribution="heavy_tailed"
),
# ⏳ Custom binning example
"years_experience": NumericalFeature(
name="years_experience",
feature_type=FeatureType.FLOAT_DISCRETIZED,
num_bins=5 # 📏 Number of bins
)
}
⚙️ Key Configuration Options
| Parameter | Description | Default | Suggested Range |
|---|---|---|---|
feature_type |
🏷️ Base feature type | FLOAT_NORMALIZED |
Choose from 4 types |
use_embedding |
🧠 Enable neural embeddings | False |
True/False |
embedding_dim |
📏 Dimensionality of embedding | 8 | 4-64 |
preferred_distribution |
📊 Hint about data distribution | None |
"normal", "log_normal", etc. |
num_bins |
🔢 Bins for discretization | 10 | 5-100 |
🔥 Power Features
Distribution-Aware Processing
Let KDP automatically detect and handle distributions:
# ✨ Enable distribution-aware processing for all numerical features
preprocessor = PreprocessingModel(
features_specs=features,
use_distribution_aware=True # 🔍 Enable distribution detection
)
Advanced Numerical Embeddings
Using advanced numerical embeddings:
# Configure numerical embeddings
preprocessor = PreprocessingModel(
features_specs={
"income": NumericalFeature(
name="income",
feature_type=FeatureType.FLOAT_RESCALED,
use_embedding=True,
embedding_dim=32,
preferred_distribution="log_normal"
)
}
)
💼 Real-World Examples
Financial Analysis
# 📈 Financial metrics with appropriate processing
preprocessor = PreprocessingModel(
features_specs={
"income": NumericalFeature(
name="income",
feature_type=FeatureType.FLOAT_RESCALED,
preferred_distribution="log_normal" # 📉 Log-normal distribution
),
"credit_score": NumericalFeature(
name="credit_score",
feature_type=FeatureType.FLOAT_NORMALIZED,
use_embedding=True,
embedding_dim=16
),
"debt_ratio": NumericalFeature(
name="debt_ratio",
feature_type=FeatureType.FLOAT_NORMALIZED,
preferred_distribution="bounded" # 📊 Bounded between 0 and 1
)
},
use_distribution_aware=True # 🧠 Smart distribution handling
)
Sensor Data
# 📡 Processing sensor readings
preprocessor = PreprocessingModel(
features_specs={
"temperature": NumericalFeature(
name="temperature",
feature_type=FeatureType.FLOAT_RESCALED,
use_embedding=True,
embedding_dim=16
),
"humidity": NumericalFeature(
name="humidity",
feature_type=FeatureType.FLOAT_NORMALIZED,
preferred_distribution="bounded" # 💧 Bounded between 0 and 100
),
"pressure": NumericalFeature(
name="pressure",
feature_type=FeatureType.FLOAT_RESCALED,
use_embedding=True,
embedding_dim=16
)
}
)
💡 Pro Tips
Understand Your Data Distribution
- Use
FLOAT_NORMALIZEDwhen your data has clear bounds (e.g., 0-100%) - Use
FLOAT_RESCALEDwhen your data has outliers (e.g., income, prices) - Use
FLOAT_DISCRETIZEDwhen your values naturally form groups (e.g., age groups)
Consider Neural Embeddings for Complex Relationships
- Enable when a simple scaling doesn't capture the pattern
- Increase embedding dimensions for more complex patterns (16→32→64)
Let KDP Handle Distribution Detection
- Enable
use_distribution_aware=Trueand let KDP automatically choose - This is especially important for skewed or multi-modal distributions
Custom Bin Boundaries
- Use
num_binsparameter to control discretization granularity - More bins = finer granularity but more parameters to learn
🔗 Related Topics
🧮 Types of Numerical Features
KDP supports different types of numerical features, each with specialized processing:
FLOAT
Basic floating-point features with default normalization
FLOAT_NORMALIZED
Values normalized to the [0,1] range using min-max scaling
FLOAT_RESCALED
Values rescaled using standardization (mean=0, std=1)
FLOAT_DISCRETIZED
Continuous values binned into discrete buckets
📊 Architecture Diagrams
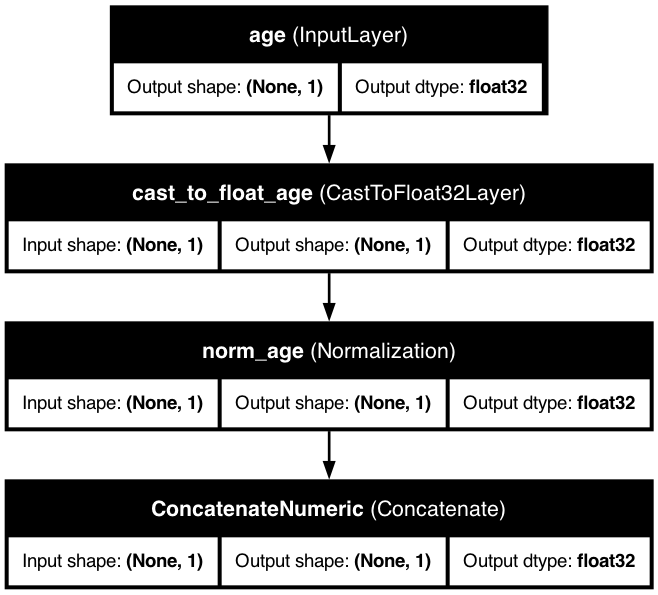
📏 Normalized Numerical Feature
Below is a visualization of a model with a normalized numerical feature:
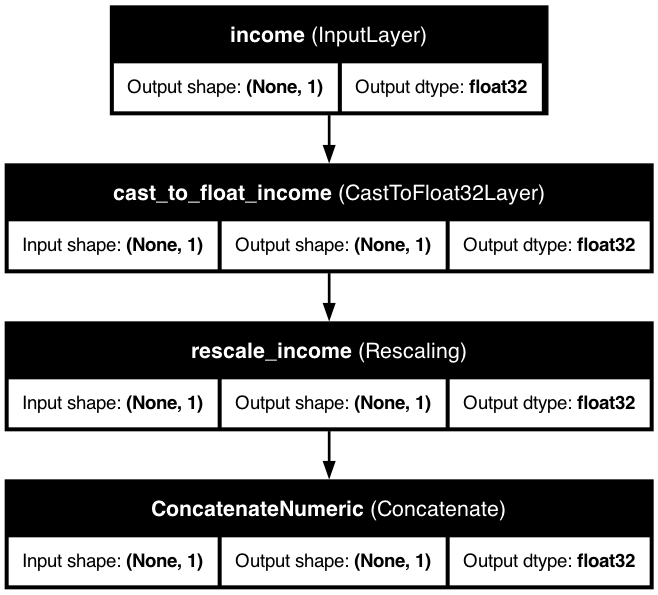
⚖️ Rescaled Numerical Feature
Below is a visualization of a model with a rescaled numerical feature:
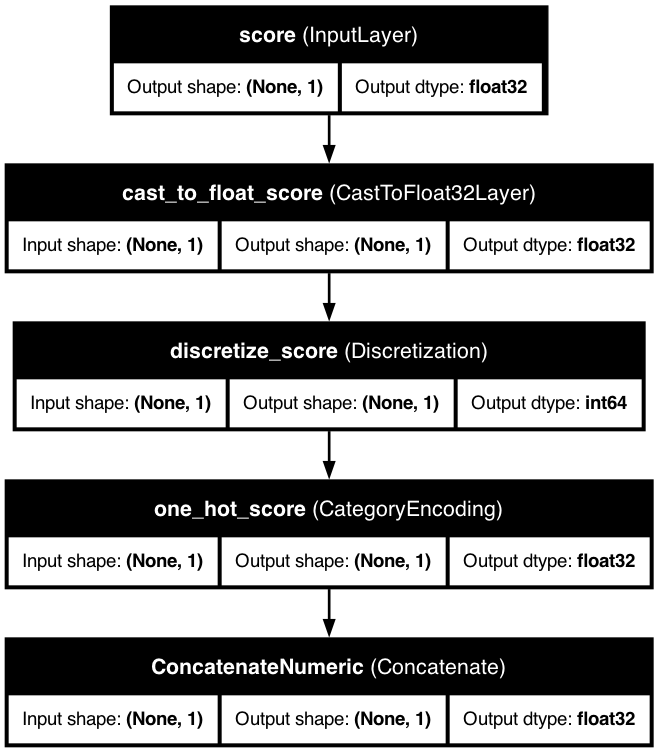
📊 Discretized Numerical Feature
Below is a visualization of a model with a discretized numerical feature:
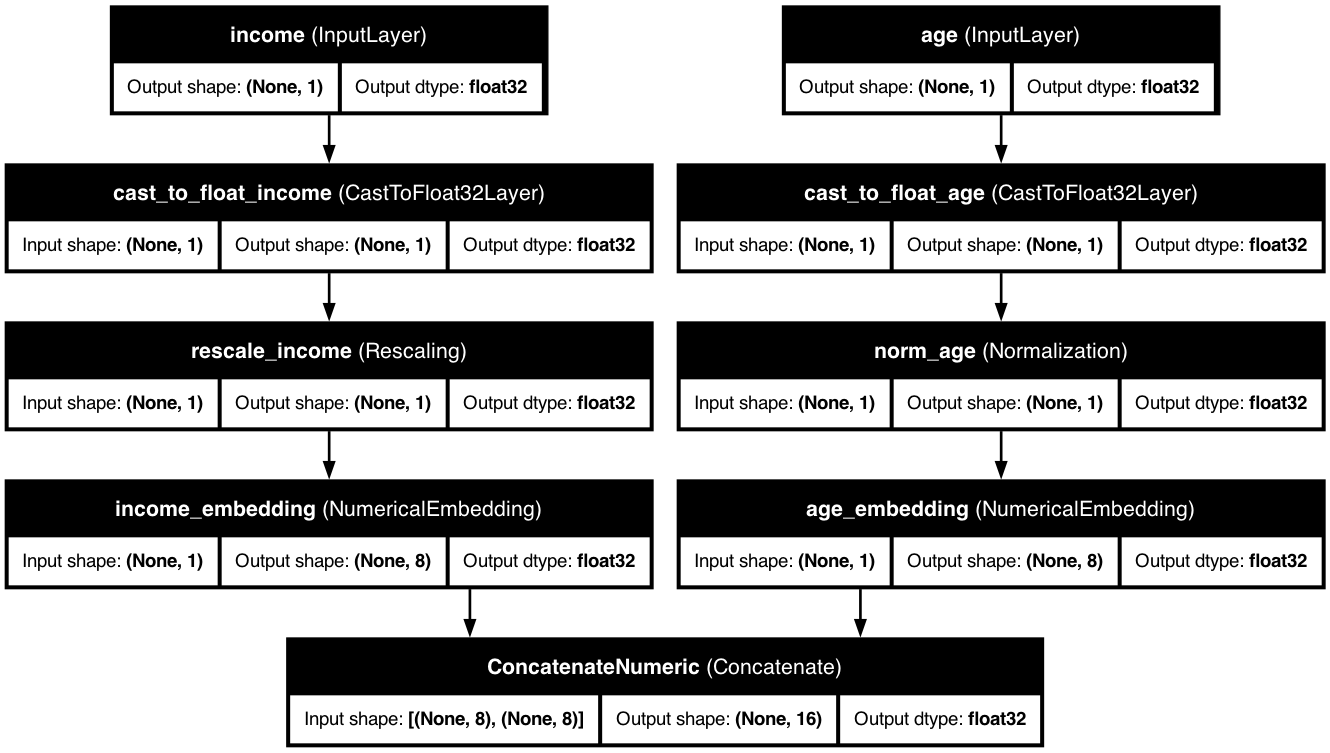
🧠 Advanced Numerical Embeddings
When using advanced numerical embeddings, the model architecture looks like this: