🔍 Passthrough Features
Passthrough Features in KDP
Handle IDs, metadata, and pre-processed data without unwanted transformations.
📋 Overview
Passthrough features allow you to include data in your model inputs without any preprocessing modifications. They're perfect for IDs, metadata, pre-processed data, and scenarios where you need to preserve exact values. With KDP v1.11.1+, you can now choose whether passthrough features are included in the main model output or kept separately for manual use.
ID Preservation
Keep product IDs, user IDs for result mapping
Metadata Handling
Include metadata without processing it
Direct Integration
Include pre-processed data without modifications
Flexible Output
Choose between processed inclusion or separate access
🚀 When to Use Passthrough Features
IDs & Identifiers
Product IDs, user IDs, transaction IDs that you need for mapping results but shouldn't influence the model
Metadata
Timestamps, source information, or other metadata needed for post-processing but not for ML
Pre-computed Features
Pre-computed embeddings or features that should be included in model processing
Raw Values
Exact original values that need to be preserved without any transformations
Feature Testing
Compare raw vs processed feature performance in experiments
💡 Two Modes of Operation
KDP v1.11.1+ introduces two distinct modes for passthrough features:
🔄 Legacy Mode (Processed Output)
When: include_passthrough_in_output=True (default for backwards compatibility)
Use case: Pre-computed features that should be part of model processing
preprocessor = PreprocessingModel(
path_data="data.csv",
features_specs=features,
include_passthrough_in_output=True # Default - backwards compatible
)
🎯 Recommended Mode (Separate Access)
When: include_passthrough_in_output=False
Use case: IDs, metadata that should be preserved but not processed
preprocessor = PreprocessingModel(
path_data="data.csv",
features_specs=features,
include_passthrough_in_output=False # Recommended for IDs/metadata
)
💡 Defining Passthrough Features
from kdp import PreprocessingModel, FeatureType
from kdp.features import PassthroughFeature
import tensorflow as tf
# Simple approach using enum
features = {
"product_id": FeatureType.PASSTHROUGH, # Will use default tf.float32
"price": FeatureType.FLOAT_NORMALIZED,
"category": FeatureType.STRING_CATEGORICAL
}
# Advanced configuration with explicit dtype
features = {
"product_id": PassthroughFeature(
name="product_id",
dtype=tf.string # Specify string for IDs
),
"user_id": PassthroughFeature(
name="user_id",
dtype=tf.int64 # Specify int for numeric IDs
),
"embedding_vector": PassthroughFeature(
name="embedding_vector",
dtype=tf.float32 # For pre-computed features
),
"price": FeatureType.FLOAT_NORMALIZED,
"category": FeatureType.STRING_CATEGORICAL
}
🏗️ Real-World Example: E-commerce Recommendation
import pandas as pd
from kdp import PreprocessingModel, FeatureType
from kdp.features import PassthroughFeature
import tensorflow as tf
# Sample e-commerce data
data = pd.DataFrame({
'product_id': ['P001', 'P002', 'P003'], # String ID - for mapping
'user_id': [1001, 1002, 1003], # Numeric ID - for mapping
'price': [29.99, 49.99, 19.99], # ML feature
'category': ['electronics', 'books', 'clothing'], # ML feature
'rating': [4.5, 3.8, 4.2] # ML feature
})
# Define features with proper separation
features = {
# IDs for mapping - should NOT influence the model
'product_id': PassthroughFeature(name='product_id', dtype=tf.string),
'user_id': PassthroughFeature(name='user_id', dtype=tf.int64),
# Actual ML features - should be processed
'price': FeatureType.FLOAT_NORMALIZED,
'category': FeatureType.STRING_CATEGORICAL,
'rating': FeatureType.FLOAT_NORMALIZED
}
# Create preprocessor with separate passthrough access
preprocessor = PreprocessingModel(
path_data="ecommerce_data.csv",
features_specs=features,
output_mode='dict',
include_passthrough_in_output=False # Keep IDs separate
)
model = preprocessor.build_preprocessor()
# Now you can:
# 1. Use the model for ML predictions (price, category, rating)
# 2. Access product_id and user_id separately for mapping results
# 3. No dtype concatenation issues between string IDs and numeric features
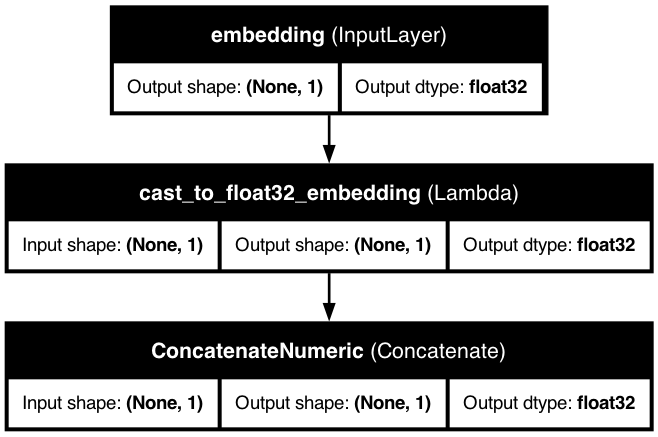
Passthrough features create input signatures but can be processed or kept separate based on your configuration.
Input Signature
Added to model inputs with proper dtype
Minimal Processing
Type casting and optional reshaping only
Concatenated
Included in main model output (grouped by dtype)
Input Signature
Added to model inputs with proper dtype
No Processing
Completely bypasses KDP transformations
Separate Access
Available separately for manual use
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name |
str | The name of the feature |
feature_type |
FeatureType | Set to FeatureType.PASSTHROUGH by default |
dtype |
tf.DType | The data type of the feature (default: tf.float32) |
include_passthrough_in_output |
bool | Whether to include in main output (True) or keep separate (False) |
# Handles both string and numeric IDs without concatenation errors
features = {
'product_id': PassthroughFeature(name='product_id', dtype=tf.string),
'user_id': PassthroughFeature(name='user_id', dtype=tf.int64),
'session_id': PassthroughFeature(name='session_id', dtype=tf.string),
'price': FeatureType.FLOAT_NORMALIZED
}
preprocessor = PreprocessingModel(
path_data="data.csv",
features_specs=features,
include_passthrough_in_output=False # No dtype mixing issues
)
# Include pre-computed features in model processing
features = {
'text_embedding': PassthroughFeature(
name='text_embedding',
dtype=tf.float32
),
'image_embedding': PassthroughFeature(
name='image_embedding',
dtype=tf.float32
),
'user_age': FeatureType.FLOAT_NORMALIZED
}
preprocessor = PreprocessingModel(
path_data="embeddings.csv",
features_specs=features,
include_passthrough_in_output=True # Include in model processing
)
# Keep metadata for post-processing without affecting the model
features = {
'timestamp': PassthroughFeature(name='timestamp', dtype=tf.string),
'source_system': PassthroughFeature(name='source_system', dtype=tf.string),
'batch_id': PassthroughFeature(name='batch_id', dtype=tf.int64),
'sales_amount': FeatureType.FLOAT_NORMALIZED,
'product_category': FeatureType.STRING_CATEGORICAL
}
preprocessor = PreprocessingModel(
path_data="sales_data.csv",
features_specs=features,
include_passthrough_in_output=False # Metadata separate from ML
)
Dtype Compatibility
When using include_passthrough_in_output=True, passthrough features are grouped by dtype to prevent concatenation errors. String and numeric passthrough features are handled separately.
Recommended Usage
Use include_passthrough_in_output=False for IDs and metadata that shouldn't influence your model. Use True only for pre-processed features that should be part of model processing.
Backwards Compatibility
The default is True to maintain backwards compatibility with existing code. New projects should explicitly choose the appropriate mode.
❌ "Cannot concatenate tensors of different dtypes"
Solution: Set include_passthrough_in_output=False for ID/metadata features, or ensure all passthrough features have compatible dtypes.
❌ "inputs not connected to outputs"
Solution: This can happen with passthrough-only models. Ensure you have at least one processed feature, or use dict mode for passthrough-only scenarios.
❌ String features showing as tf.float32
Solution: Explicitly specify dtype in PassthroughFeature: dtype=tf.string
Reduce Model Complexity
Use include_passthrough_in_output=False for IDs to keep your model focused on actual ML features
Clear Separation
Separate concerns: IDs for mapping, features for ML, metadata for analysis
Choose the Right Mode
Legacy mode for pre-computed features, recommended mode for identifiers and metadata